File system performance: Difference between revisions
From genomewiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==test procedure== | |||
Testing filesystem performance read/write numbers of files into overloaded directory with up | Testing filesystem performance read/write numbers of files into overloaded directory with up | ||
to 7 million files. | to 7 million files. | ||
* start with empty directory | |||
* writing test uses kent source library functions to obtain a unique filename in | |||
the directory | |||
==/dev/shm/ tmpfs in memory filesystem== | ==/dev/shm/ tmpfs in memory filesystem== | ||
Revision as of 23:03, 31 May 2017
test procedure
Testing filesystem performance read/write numbers of files into overloaded directory with up to 7 million files.
- start with empty directory
- writing test uses kent source library functions to obtain a unique filename in
the directory
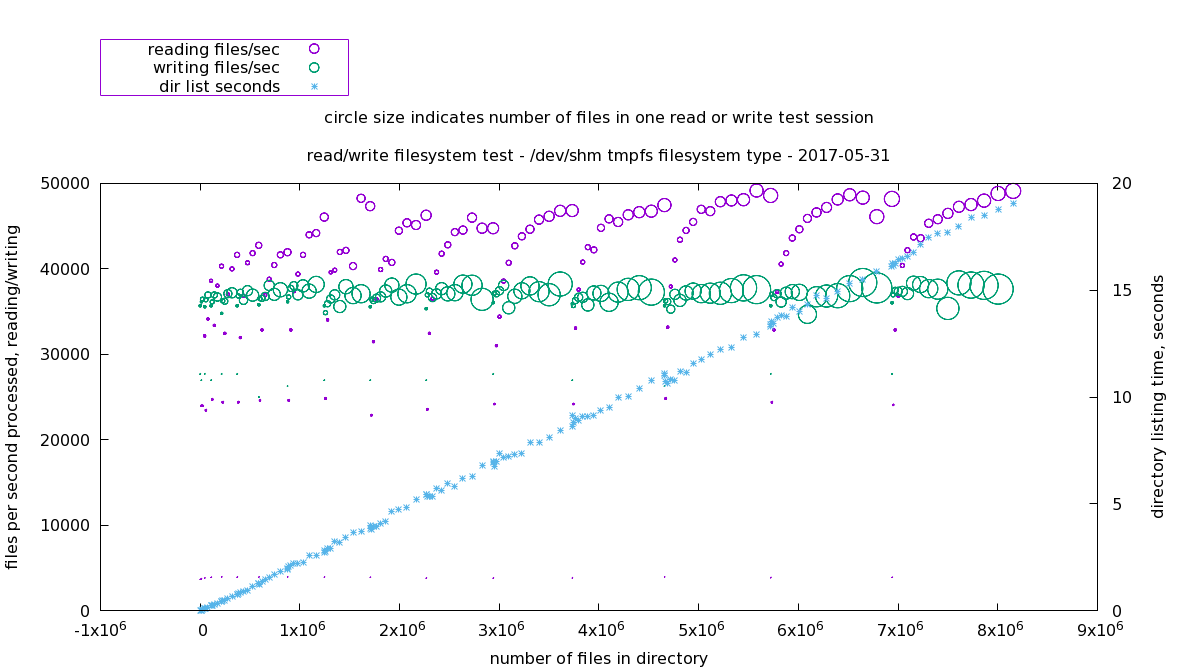
/dev/shm/ tmpfs in memory filesystem
The null model test. This is the RAM memory filesystem '/dev/shm/'. Performance remains constant despite numbers of files in the directory.
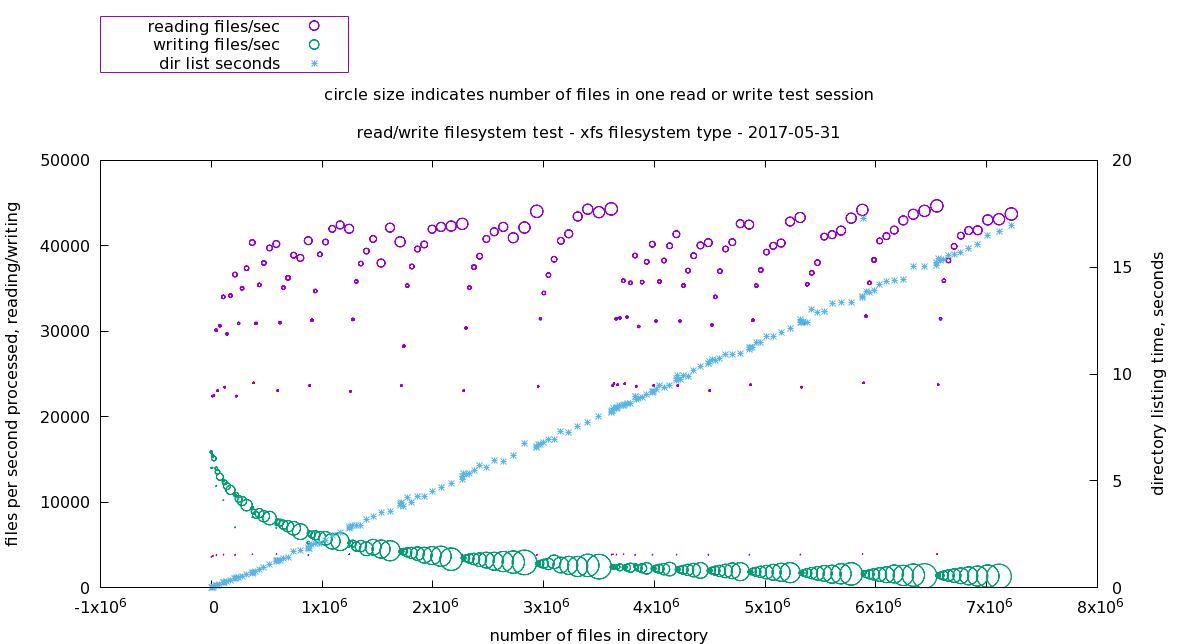
xfs filesystem
Writing performance declines rapidly, reading performance remains constant.
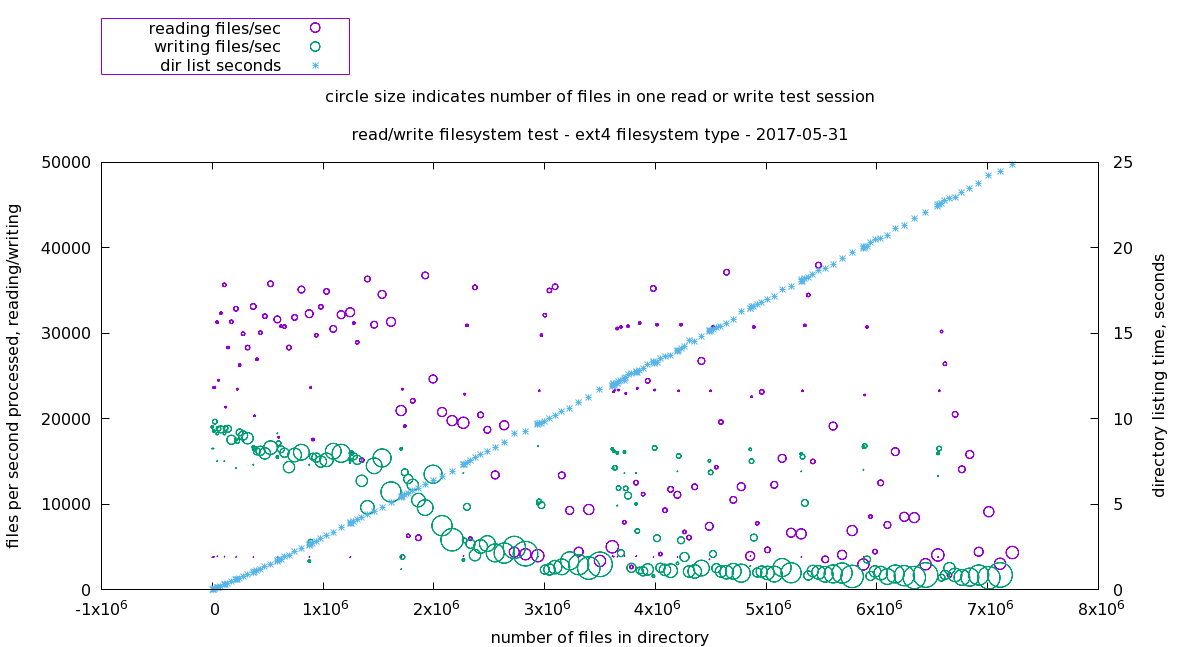
ext4 filesystem
Both read and write performance drop off between one and two million files in the directory.