File system performance: Difference between revisions
From genomewiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
(adding btrfs) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* start with empty directory | * start with empty directory | ||
* writing test uses kent source library functions to obtain | * writing test uses kent source library trash directory functions to obtain unique filenames in the directory | ||
* start with fileCount = 1,024 | |||
* begin loop | |||
* writing fileCount number of files of approximate size 16,384 bytes (bell curve of sizes) | |||
* then randomly reads fileCount/2 number of files | |||
* increment fileCount by 10,000 | |||
* after first time through this loop | |||
** second inner loop repeats this entire procedure from 1,024 number of files up to outer loop count | |||
* repeat outer loop | |||
The reading test procedure: | |||
* read in file names for entire directory | |||
* looping for fileCount | |||
** randomly select a file from the list | |||
** stat the file to obtain its size | |||
** read the file into a memory buffer | |||
** close file handle | |||
* repeat loop | |||
Recording the time for obtaining the list of file names for the directory, | |||
and the time for reading/writing fileCount number of files, as well as counting | |||
the number of bytes read/written. | |||
==/dev/shm/ tmpfs in memory filesystem== | ==/dev/shm/ tmpfs in memory filesystem== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 46: | ||
[[Image:Ext4_fs_readWrite_performance.png]] | [[Image:Ext4_fs_readWrite_performance.png]] | ||
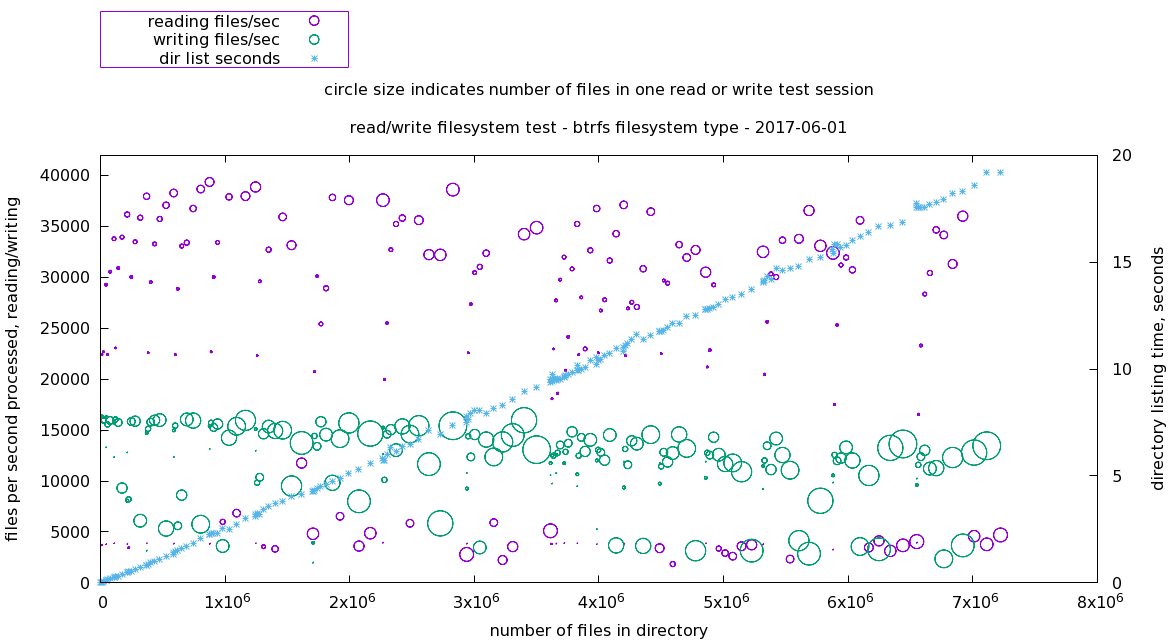
==btrfs filesystem== | |||
Both read and write performance are mostly stable despite high file count. | |||
[[Image:Btrfs_filesystem_readWrite_performance.png]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:19, 2 June 2017
test procedure
Testing filesystem performance read/write numbers of files into overloaded directory with up to 7 million files.
- start with empty directory
- writing test uses kent source library trash directory functions to obtain unique filenames in the directory
- start with fileCount = 1,024
- begin loop
- writing fileCount number of files of approximate size 16,384 bytes (bell curve of sizes)
- then randomly reads fileCount/2 number of files
- increment fileCount by 10,000
- after first time through this loop
- second inner loop repeats this entire procedure from 1,024 number of files up to outer loop count
- repeat outer loop
The reading test procedure:
- read in file names for entire directory
- looping for fileCount
- randomly select a file from the list
- stat the file to obtain its size
- read the file into a memory buffer
- close file handle
- repeat loop
Recording the time for obtaining the list of file names for the directory, and the time for reading/writing fileCount number of files, as well as counting the number of bytes read/written.
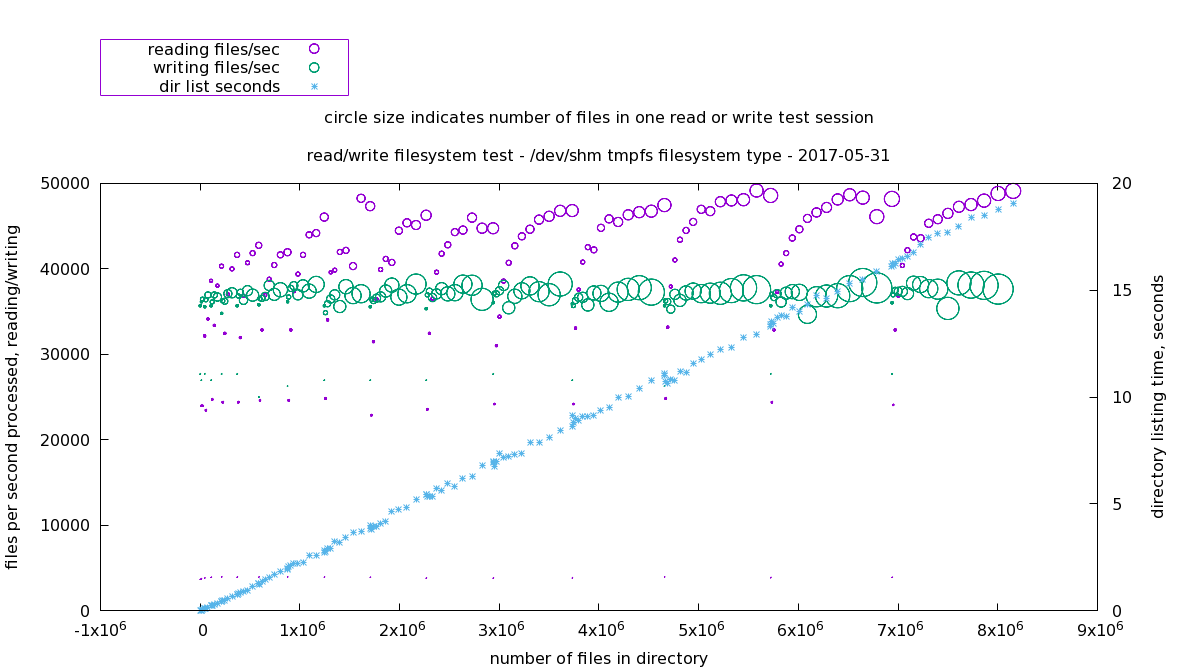
/dev/shm/ tmpfs in memory filesystem
The null model test. This is the RAM memory filesystem '/dev/shm/'. Performance remains constant despite numbers of files in the directory.
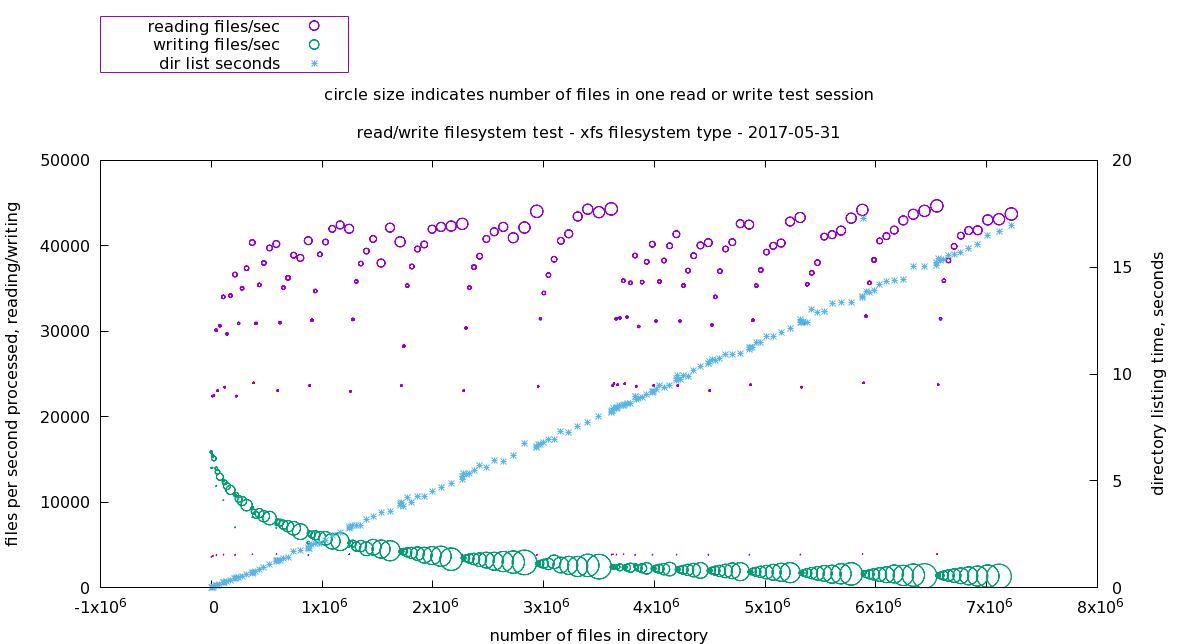
xfs filesystem
Writing performance declines rapidly, reading performance remains constant.
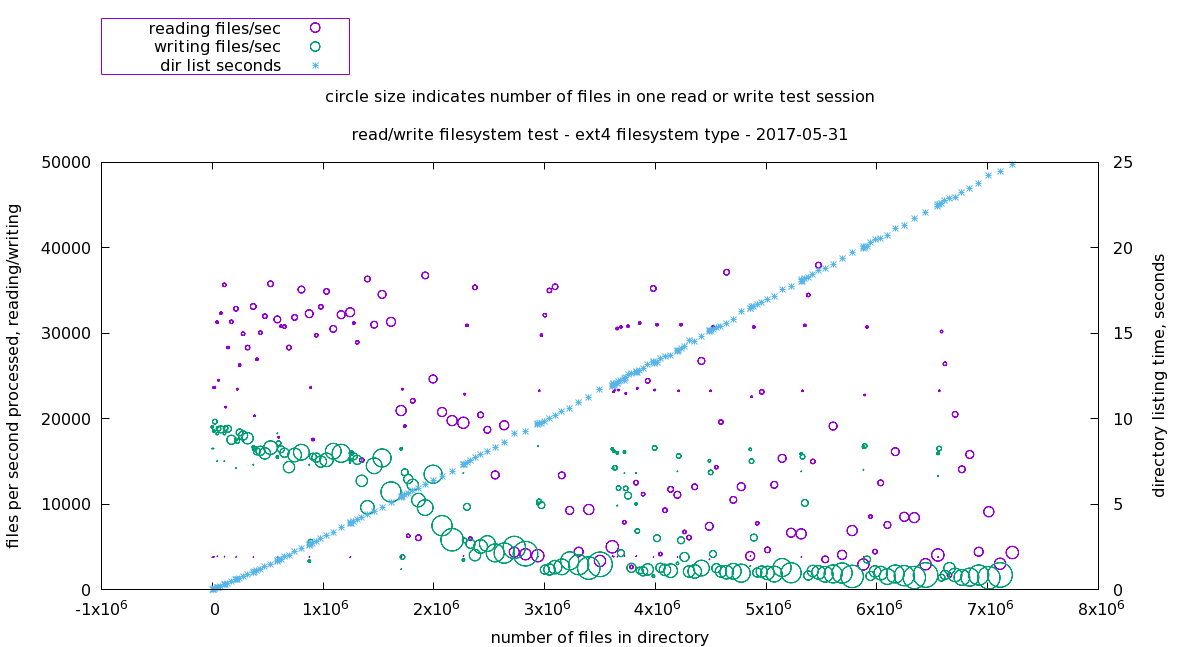
ext4 filesystem
Both read and write performance drop off between one and two million files in the directory.
btrfs filesystem
Both read and write performance are mostly stable despite high file count.